Waveshare 65K RGB General 1.28inch Round LCD Display Module
Product Link
Introduction
1.28inch LCD Display Module, IPS Screen, 65K RGB, 240 × 240 Resolution, SPI Interface.
Specification
Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V
Interface: SPI
LCD type: IPS
Controller: GC9A01
Resolution: 240 (H)RGB x 240(V)
Display size: Φ32.4mm
Pixel size: 0.135(H)x 0.135(V)mm
Dimension: 40.4 × 37.5(mm) Φ37.5(mm)
Interface Description
Raspberry Pi
Please connect the LCD to your Raspberry Pi by the 8PIN cable according to the table below Use the pin header or PH2.0 8PIN interface, you need to connect according to the following table
BCM2835
Board
VCC
3.3V
3.3V
GND
GND
GND
DIN
MOSI
19
CLK
SCLK
23
CS
CE0
24
DS
25
22
RST
27
13
BL
18
12
The 1.28inch LCD uses the PH2.0 8PIN interface, which can be connected to the Raspberry Pi according to the above table: (Please connect according to the pin definition table. The color of the wiring in the picture is for reference only, and the actual color shall prevail.)

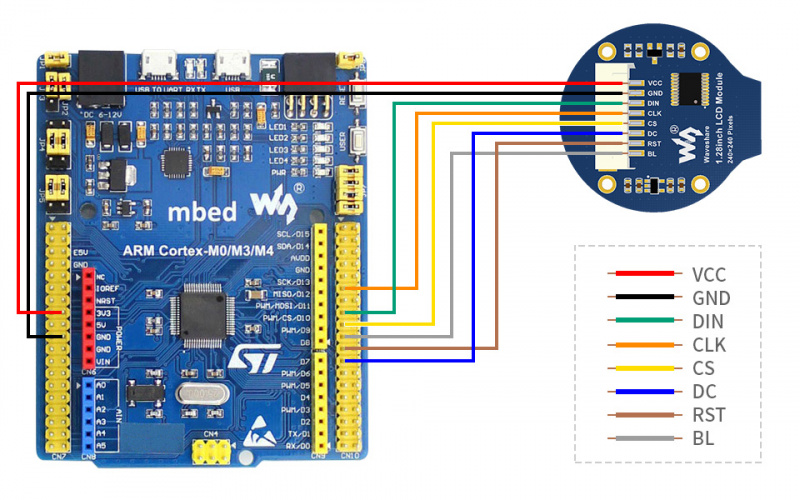
STM32
The example we provide is based on STM32F103RBT6, and the connection method provided is also the corresponding pin of STM32F103RBT6. If you need to transplant the program, please connect according to the actual pin.
VCC
3.3V
GND
GND
DIN
PA7
CLK
PA5
CS
PB6
DC
PA8
RST
PA9
BL
PC7
Take the XNUCLEO-F103RB development board developed by our company as an example, the connection is as follows:
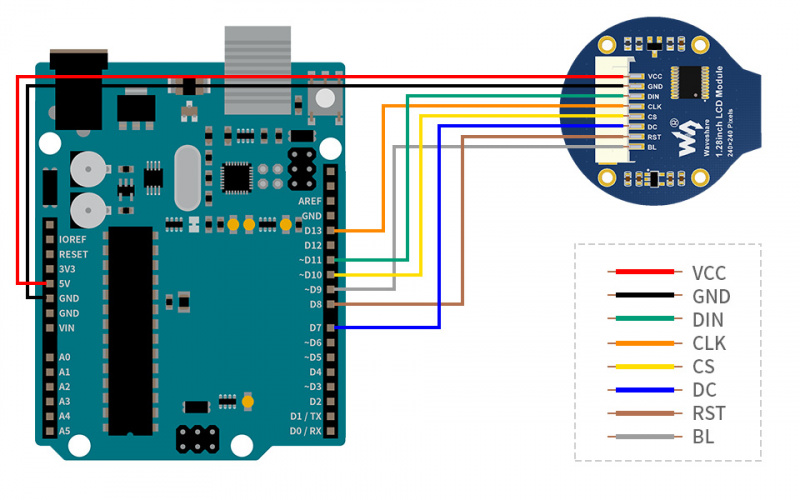
Arduino
VCC
5V
GND
GND
DIN
D11
CLK
D13
CS
D10
DC
D7
RST
D8
BL
D9
The connection diagram is as follows (click to enlarge):
LCD & Controller
The built-in driver used in this LCD is GC9A01, with a resolution of 240RGB×240 dots, 129,600 bytes of GRAM inside. This LCD supports 12/16/18-bit data bus MCU interface, namely the formats of RGB444, RGB565, RGB666, which are commonly used. Most of the LCD controllers can debug their communication ways such as by 8080 parallel interfaces, three-wire SPI, four-wire SPI, and so on. This LCD adopts a four-wire SPI communication interface, which can greatly save the GPIO port, and the communication speed will be faster.
Maybe you have doubts that as the screen is circular, which point is the first pixel? How to determine the coordinates?
In fact, you can presume that a square screen draws an inscribed circle in it. We only display the content in this inscribed circle, and the pixels beside the square are deleted. The same is true for most of the circular LCDs on the market.
Communication Protocol
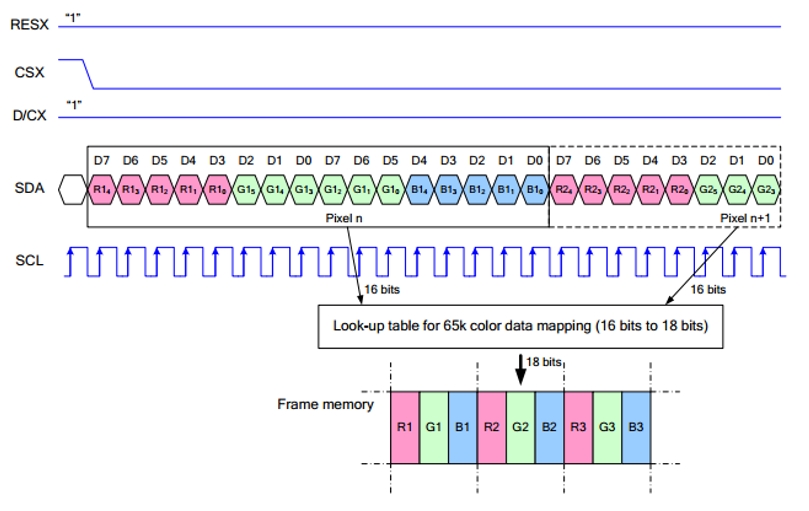
Note: Different from the traditional SPI protocol: the data line sent from the slave to the host is hidden as the LCD only needs to be displayed. Please refer to the table on Datasheet Page 105. RESX: reset, it is pulled low when the module is powered on, and it is usually set to 1. CSX: the slave chip selection and the chip will be enabled only when CS is low. D/CX: the data/command control pin of the chip, write command when DC = 0, write data when DC=1 SDA: the transmitted data, that is, RGB data; SCL: the SPI communication clock. For SPI communication, data is transmitted with timing, that is, the combination of clock phase (CPHA) and clock polarity (CPOL): The level of CPHA determines whether the data of the serial synchronization clock is collected on the first clock transition edge or the second clock transition edge. When CPHA = 0, data acquisition is performed on the first transition edge; The level of CPOL determines the idle state level of the serial synchronous clock. CPOL = 0, which is a low level. As can be seen from the figure, when the first falling edge of SCLK starts to transmit data, 8bit data is transmitted in one clock cycle, using SPI0, bit-by-bit transmission, high-order first, and low-order at last.
Working with Raspberry Pi
Enable SPI interface
PS: If you are using the system of the Bullseye branch, you need to change "apt-get" to "apt", the system of the Bullseye branch only supports Python3.

Open terminal, use command to enter the configuration page
Reboot Raspberry Pi:
Please make sure the SPI is not occupied by other devices, you can check in the middle of /boot/config.txt
Install Library
If you use bookworm system, only the lgpio library is available, bcm2835 and wiringPi libarary cannot be installed or used. Please note that the python library does not need to install, you can directly run the demo.
BCM2835
WiringPi
lgpio
Python
Download Examples
Open Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command
Run the demo codes
Please go into the RaspberryPi directory (demo codes) first and run the commands in terminal
C codes
Re-compile the demo codes
The test program of all screens can be called directly by entering the corresponding size
Depending on the LCD, one of the following commands should be entered:
python
Enter the python program directory and run the command ls -l
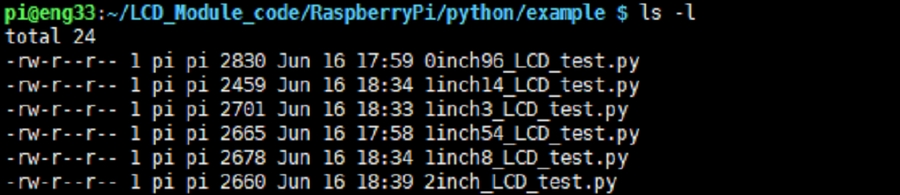 Test programs for all screens can be viewed, sorted by size:
0inch96_LCD_test.py: 0.96inch LCD test program
1inch14_LCD_test.py: 1.14inch LCD test program
1inch28_LCD_test.py: 1.28inch LCD test program
1inch3_LCD_test.py: 1.3inch LCD test program
1inch47_LCD_test.py: 1.47inch LCD test program
1inch54_LCD_test.py: 1.54inchLCD test program
1inch8_LCD_test.py: 1.8inch LCD test program
2inch_LCD_test.py: 2inch LCD test program
2inch4_LCD_test.py: 2inch4 LCD test program
Test programs for all screens can be viewed, sorted by size:
0inch96_LCD_test.py: 0.96inch LCD test program
1inch14_LCD_test.py: 1.14inch LCD test program
1inch28_LCD_test.py: 1.28inch LCD test program
1inch3_LCD_test.py: 1.3inch LCD test program
1inch47_LCD_test.py: 1.47inch LCD test program
1inch54_LCD_test.py: 1.54inchLCD test program
1inch8_LCD_test.py: 1.8inch LCD test program
2inch_LCD_test.py: 2inch LCD test program
2inch4_LCD_test.py: 2inch4 LCD test program
Just run the program corresponding to the screen, the program supports python2/3
API Description
The RaspberryPi series can share a set of programs, because they are all embedded systems, and the compatibility is relatively strong. The program is divided into bottom-layer hardware interface, middle-layer LCD screen driver, and upper-layer application;
C
Hardware Interface
We have carried out the low-level encapsulation, if you need to know the internal implementation can go to the corresponding directory to check, for the reason the hardware platform and the internal implementation are different. You can open DEV_Config.c(.h) to see definitions,which in the directory RaspberryPi\c\lib\Config.
Data type:
Module initialization and exit processing.
GPIO read and write:
SPI write data:
Upper application
If you need to draw pictures or display Chinese and English characters, we provide some basic functions here about some graphics processing in the directory RaspberryPi\c\lib\GUI\GUI_Paint.c(.h).
The fonts can be found in RaspberryPi\c\lib\Fonts directory.
New Image Properties: Create a new image buffer, this property includes the image buffer name, width, height, flip Angle, and color.
Select image buffer: The purpose of the selection is that you can create multiple image attributes, there can be multiple images buffer, you can select each image you create.
Image Rotation: Set the rotation Angle of the selected image, preferably after Paint_SelectImage(), you can choose to rotate 0, 90, 180, 270.
Image mirror flip: Set the mirror flip of the selected image. You can choose no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, or image center mirror
Set points of the display position and color in the buffer: here is the core GUI function, processing points display position and color in the buffer.
Image buffer fill color: Fills the image buffer with a color, usually used to flash the screen into blank.
The fill color of a certain window in the image buffer: the image buffer part of the window filled with a certain color, usually used to fresh the screen into blank, often used for time display, fresh the last second of the screen.
Draw point: In the image buffer, draw points on (Xpoint, Ypoint), you can choose the color, the size of the point, the style of the point.
Draw line: In the image buffer, draw line from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width and the style of the line.
Draw rectangle: In the image buffer, draw a rectangle from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width of the line, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle.
Draw circle: In the image buffer, draw a circle of Radius with (X_Center Y_Center) as the center. You can choose the color, the width of the line, and whether to fill the inside of the circle.
Write Ascii character: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write an Ascii character, you can select Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Write English string: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of English characters, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Write Chinese string: in the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of Chinese characters, you can choose character font, font foreground color, and font background color of the GB2312 encoding.
Write numbers: In the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Display time: in the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display time,you can choose Ascii visual character font, font foreground color, font background color.
Read the local bmp image and write it to the cache.
For Linux operating systems such as Raspberry Pi, you can read and write pictures. For Raspberry Pi, in the directory: RaspberryPi\c\lib\GUI\GUI_BMPfile.c(.h).
Testing Code for Users
For Raspberry Pi, in the directory: RaspberryPi\c\examples, for all the test code;
If you need to run the 0.96-inch LCD test program, you need to add 0.96 as a parameter when running the main demo. Re-execute in Linux command mode as follows:
Python (for Raspberry Pi)
Works with python and python3. For python, his calls are not as complicated as C. Raspberry Pi: RaspberryPi\python\lib\
lcdconfig.py
Module initialization and exit processing.
GPIO read and write:
SPI write data.
xxx_LCD_test.py (xxx indicates the size, if it is a 0.96inch LCD, it is 0inch96_LCD_test.py, and so on)
python is in the following directory: Raspberry Pi: RaspberryPi\python\examples\
If your python version is python2 and you need to run the 0.96inch LCD test program, re-execute it as follows in linux command mode:
If your python version is python3 and you need to run the 0.96inch LCD test program, re-execute the following in linux command mode:
About Rotation Settings
If you need to set the screen rotation in the python program, you can set it by the statement im_r= image1.rotate(270).
Rotation effect, take 1.54 as an example, the order is 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°

GUI Functions
Python has an image library PIL official library link, it does not need to write code from the logical layer like C and can directly call to the image library for image processing. The following will take a 1.54-inch LCD as an example, we provide a brief description of the demo.
It needs to use the image library and install the library.
And then import the library
Among them, Image is the basic library, ImageDraw is the drawing function, and ImageFont is the text function.
Define an image cache to facilitate drawing, writing, and other functions on the picture.
The first parameter defines the color depth of the image, which is defined as "1" to indicate the bitmap of one-bit depth. The second parameter is a tuple that defines the width and height of the image. The third parameter defines the default color of the buffer, which is defined as "WHITE".
Create a drawing object based on Image1 on which all drawing operations will be performed on here.
Draw a line.
The first parameter is a four-element tuple starting at (0, 0) and ending at (127,0). Draw a line. Fill ="0" means the color of the line is white.
Draw a rectangle.
The first argument is a tuple of four elements. (20,10) is the coordinate value in the upper left corner of the rectangle, and (70,60) is the coordinate value in the lower right corner of the rectangle. Fill =" WHITE" means BLACK inside, and outline="BLACK" means the color of the outline is black.
Draw a circle.
Draw an inscribed circle in the square, the first parameter is a tuple of 4 elements, with (150, 15) as the upper left corner vertex of the square, (190, 55) as the lower right corner vertex of the square, specifying the level median line of the rectangular frame is the angle of 0 degrees, the second parameter indicates the starting angle, the third parameter indicates the ending angle, and fill = 0 indicates that the color of the line is white. If the figure is not square according to the coordination, you will get an ellipse.
Besides the arc function, you can also use the chord function for drawing a solid circle.
The first parameter is the coordination of the enclosing rectangle. The second and third parameters are the beginning and end degrees of the circle. The fourth parameter is the fill color of the circle.
Character.
The ImageFont module needs to be imported and instantiated:
You can use the fonts of Windows or other fonts which is in ttc format.. Note: Each character library contains different characters; If some characters cannot be displayed, it is recommended that you can refer to the encoding set ro used. To draw English characters, you can directly use the fonts; for Chinese characters, you need to add a symbol u:
The first parameter is a tuple of 2 elements, with (40, 50) as the left vertex, the font is Font2, and the fill is the font color. You can directly make fill = "WHITE", because the regular color value is already defined Well, of course, you can also use fill = (128,255,128), the parentheses correspond to the values of the three RGB colors so that you can precisely control the color you want. The second sentence shows Micro Snow Electronics, using Font3, the font color is white.
read local image
The parameter is the image path.
Other functions.
For more information, you can refer to http://effbot.org/imagingbook pil
Using with STM32
Software description
The demo is developed based on the HAL library. Download the demo, find the STM32 program file directory, and open the LCD_demo.uvprojx in the STM32\STM32F103RBT6\MDK-ARM directory to check the program.

Open main.c, you can see all the test programs, remove the comments in front of the test programs on the corresponding screen, and recompile and download.

LCD_0in96_test() 0.96inch LCD test program LCD_1in14_test() 1.14inch LCD test program LCD_1in28_test() 1.28inch LCD test program LCD_1in3_test() 1.3 inch LCD test program LCD_1in54_test() 1.54inch LCD test program LCD_1in8_test() 1.8inch LCD test program LCD_2in_test() 2inch LCD test program
Program Description
Underlying hardware interface
Data type
Module initialization and exit processing
Write and read GPIO
SPI write data
The upper application
For the screen, if you need to draw pictures, display Chinese and English characters, display pictures, etc., you can use the upper application to do, and we provide some basic functions here about some graphics processing in the directory STM32\STM32F103RB\User\GUI_DEV\GUI_Paint.c(.h) Note: Because of the size of the internal RAM of STM32 and arduino, the GUI is directly written to the RAM of the LCD.

The character font which GUI dependent is in the directory STM32\STM32F103RB\User\Fonts

New Image Properties: Create a new image property, this property includes the image buffer name, width, height, flip Angle, color.
Set the clear screen function, usually call the clear function of LCD directly.
Set the drawing pixel function
Select image buffer:the purpose of the selection is that you can create multiple image attributes, image buffer can exist multiple, you can select each image you create.
Image Rotation: Set the selected image rotation Angle, preferably after Paint_SelectImage(), you can choose to rotate 0, 90, 180, 270.
Image mirror flip: Set the mirror flip of the selected image. You can choose no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror, or image center mirror.
Set points of display position and color in the buffer: here is the core GUI function, processing points display position and color in the buffer.
Image buffer fill color: Fills the image buffer with a color, usually used to flash the screen into blank.
Image buffer part of the window filling color: the image buffer part of the window filled with a certain color, generally as a window whitewashing function, often used for time display, whitewashing on a second
Draw points: In the image buffer, draw points on (Xpoint, Ypoint), you can choose the color, the size of the point, the style of the point.
Line drawing: In the image buffer, line from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, line width, line style.
Draw rectangle: In the image buffer, draw a rectangle from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width of the line, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle.
Draw circle: In the image buffer, draw a circle of Radius with (X_Center Y_Center) as the center. You can choose the color, the width of the line, and whether to fill the inside of the circle.
Write Ascii character: In the image buffer, at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write an Ascii character, you can select Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Write English string: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of English characters, can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Write Chinese string: in the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of Chinese characters, you can choose GB2312 encoding character font, font foreground color, font background color.
Write numbers: In the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Display time: in the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display time,you can choose Ascii visual character font, font foreground color, font background color.
Arduino Software Description
Note: The demos are all tested on Arduino uno. If you need other types of Arduino, you need to determine whether the connected pins are correct. Template: Arduino IDE Installation Steps
Run program
In the product encyclopedia interface download the program, and then unzip it. The Arduino program is located at ~/Arduino/…
Please select the corresponding program according to the LCD screen model to open
You can view test programs for all screen sizes, sorted by size: For example, 1.54inch LCD Module. Open the LCD_1inch54 folder and run the LCD_1inch54.ino file. Open the program, select the development board model Arduino UNO
Select the corresponding COM port
Then click to compile and download

Program Description
Document Introduction
Take Arduino UNO controlling a 1.54-inch LCD as an example, open the Arduino\LCD_1inch54 directory:
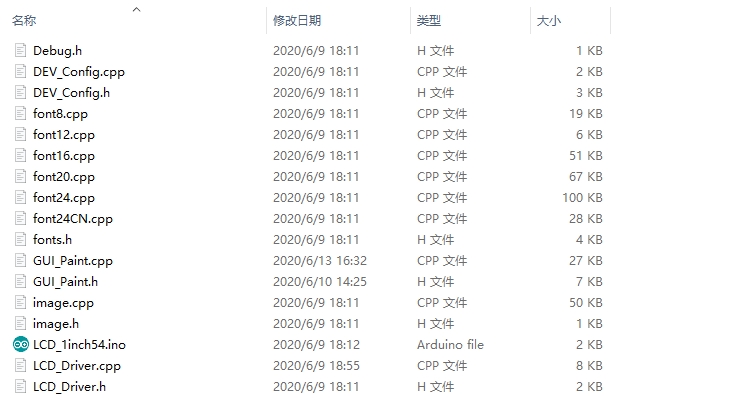
Of which: LCD_1inch54.ino: open with Arduino IDE; LCD_Driver.cpp(.h): is the driver of the LCD screen; DEV_Config.cpp(.h): It is the hardware interface definition, which encapsulates the read and write pin levels, SPI transmission data, and pin initialization; font8.cpp, font12.cpp, font16.cpp, font20.cpp, font24.cpp, font24CN.cpp, fonts.h: fonts for characters of different sizes; image.cpp(.h): is the image data, which can convert any BMP image into a 16-bit true color image array through Img2Lcd (downloadable in the development data). The program is divided into bottom-layer hardware interface, middle-layer LCD screen driver, and upper-layer application;
Underlying hardware interface
The hardware interface is defined in the two files DEV_Config.cpp(.h), and functions such as read and write pin level, delay, and SPI transmission are encapsulated.
write pin level
The first parameter is the pin, and the second is the high and low level.
Read pin level
The parameter is the pin, and the return value is the level of the read pin.
Delay
millisecond level delay.
SPI output data
The parameter is char type, occupying 8 bits.
The upper application
For the screen, if you need to draw pictures, display Chinese and English characters, display pictures, etc., you can use the upper application to do, and we provide some basic functions here about some graphics processing in the directory GUI_Paint.c(.h) Note: Because of the size of the internal RAM of STM32 and arduino, the GUI is directly written to the RAM of the LCD.

The fonts used by the GUI all depend on the font*.cpp(h) files under the same file

New Image Properties: Create a new image property, this property includes the image buffer name, width, height, flip Angle, color.
Set the clear screen function, usually call the clear function of LCD directly.
Set the drawing pixel function.
Select image buffer:the purpose of the selection is that you can create multiple image attributes, image buffer can exist multiple, you can select each image you create.
Image Rotation: Set the selected image rotation Angle, preferably after Paint_SelectImage(), you can choose to rotate 0, 90, 180, 270.
Image mirror flip: Set the mirror flip of the selected image. You can choose no mirror, horizontal mirror, vertical mirror,or image center mirror.
Set points of display position and color in the buffer: here is the core GUI function, processing points display position and color in the buffer.
Image buffer fill color: Fills the image buffer with a color, usually used to flash the screen into blank.
Draw points: In the image buffer, draw points on (Xpoint, Ypoint), you can choose the color, the size of the point, the style of the point.
Line drawing: In the image buffer, line from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, line width, line style.
Draw rectangle: In the image buffer, draw a rectangle from (Xstart, Ystart) to (Xend, Yend), you can choose the color, the width of the line, whether to fill the inside of the rectangle.
Draw circle: In the image buffer, draw a circle of Radius with (X_Center Y_Center) as the center. You can choose the color, the width of the line, and whether to fill the inside of the circle.
Write Ascii character: In the image buffer, at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write an Ascii character, you can select Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Write English string: In the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of English characters, can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Write Chinese string: in the image buffer, use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of Chinese characters, you can choose GB2312 encoding character font, font foreground color, font background color.
Write numbers: In the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers, you can choose Ascii visual character library, font foreground color, font background color.
Write numbers with decimals: at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, write a string of numbers with decimals, you can choose Ascii code visual character font, font foreground color, font background color
Display time: in the image buffer,use (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display time,you can choose Ascii visual character font, font foreground color, font background color.
Display image: at (Xstart Ystart) as the left vertex, display an image whose width is W_Image and height is H_Image;
VisionFive2
Adaptive Model
Hardware Connection
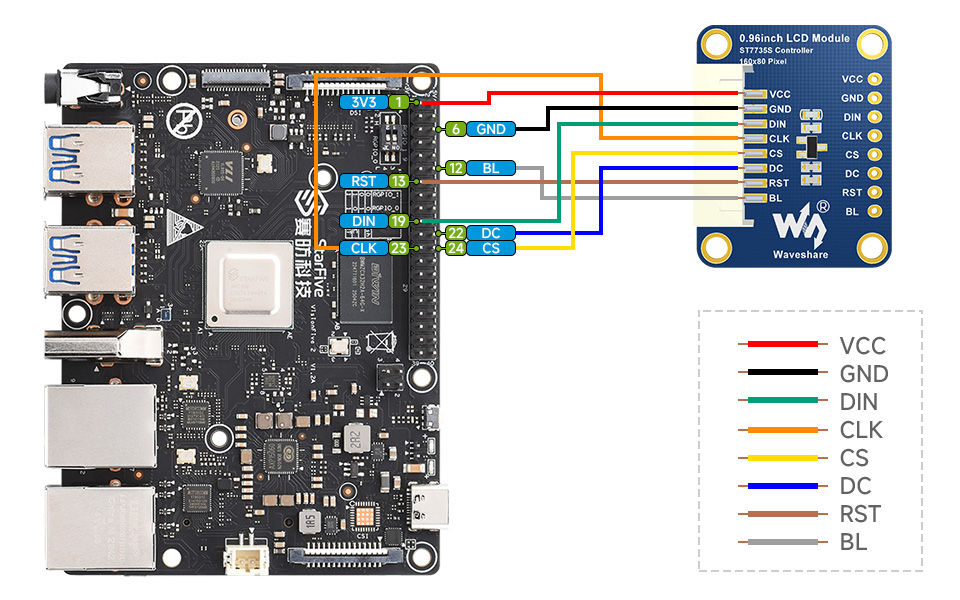
VCC
3.3V
GND
GND
DIN
19
CLK
23
CS
24
DC
22
RST
13
BL
12
Install Corresponding Libraries
Demo Download
Run the Corresponding Demo According to the Screen You Purchased
Resources
Documents
Software
Demo Codes
3D Drawing
FAQ
Last updated
Was this helpful?