Waveshare SIM7600CE-CNSE 4G HAT for Raspberry Pi 4G 3G 2G GNSS
Product Link
Introduction
The SIM7600CE-CNSE 4G HAT is a hardware accessory designed for use with compatible development boards or microcontrollers. It is a communication module that provides 4G connectivity, allowing devices to access the internet and cellular networks. The "HAT" in its name stands for "Hardware Attached on Top," which indicates that it is designed to be easily attached to the top of a development board, such as a Raspberry Pi, providing additional functionality. The SIM7600CE-CNSE specifically refers to the model of the 4G module, which is manufactured by SIMCom, a company that specializes in wireless communication modules. This particular module supports various cellular network standards and can be used for a wide range of applications, including IoT devices, remote monitoring systems, and more.

Features
40PIN GPIO extension header for connecting Jetson Nano.
Supports dial-up, telephone calls, SMS, mail, TCP, UDP, DTMF, HTTP, FTP, etc.
Supports GPS, BeiDou, Glonass, and LBS base station positioning.
Onboard USB interface, to test AT Commands, get GPS positioning data, and so on.
Breakout UART control pins, to connect with host boards like Arduino/STM32.
Onboard CP2102 USB to UART converter, for serial debugging.
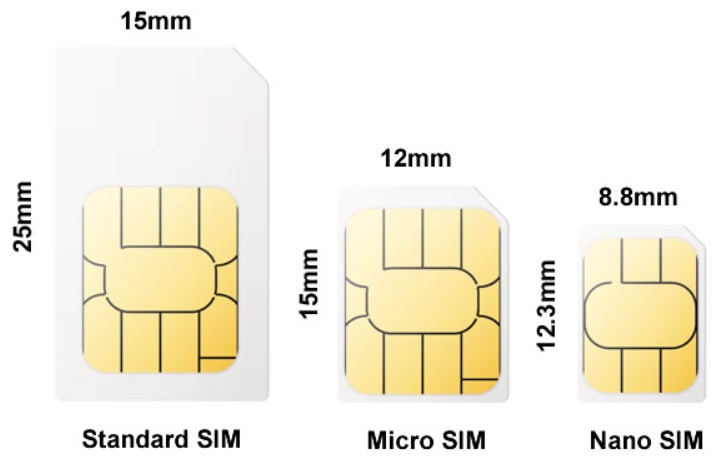
SIM card slot, supports 1.8V/3V SIM card.
Onboard TF card slot, which can be used to store files, text messages, and other data.
Onboard audio jack and audio decoder chip, for making telephone calls.
2 x LED indicators, easy to monitor the working status.
Onboard voltage translator, the operating voltage can be configured to 3.3V or 5V via jumper.
Baudrate: 300bps ~ 4Mbps (default: 115200bps)
Autobauding baudrate: 9600bps ~ 115200bps.
Comes with online resources and manuals (example demos such as Raspberry/Jetson Nano/Arduino/STM32).
Specifications

Pinout


Dimensions

How to Use
RPi Demo
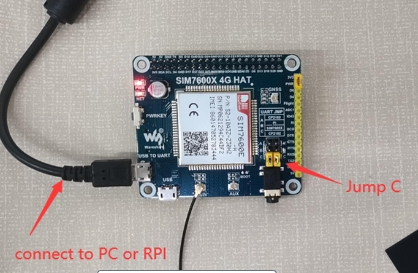
Hardware Connection
pin connection diagram with Raspberry Pi

SIM7600X 4G HAT has onboard Raspberry Pi GPIO interface, which can be directly inserted into various versions of Raspberry Pi; the following table shows the connection between Raspberry Pi pins and module pins (Raspberry Pi 3rd Generation B+):
5V
5V
GND
GND
RXD
TXD (corresponding to 14 of BCM)
TXD
RXD (corresponding to 15 of BCM)
PWR
P22 (corresponding to P6 of BCM)
FLIGHTMODE
P7 (corresponding to P4 of BCM), enter flight mode when pulled high
* FLIGHTMODE is wired to pull up and will enter into flight mode.
Raspberry Pi initialization settings
To ensure that the SIM7600X 4G HAT can work normally after being connected to the Raspberry Pi, it is necessary to initialize the level output of some pins of the Raspberry Pi. The specific operations are as follows:
Download sample demo, after decompression, rename the c folder under the Raspberry folder to SIM7600X, Then copy the entire SIM7600X folder to the Raspberry Pi /home/pi directory.
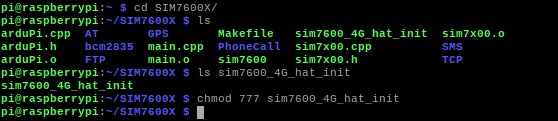
The command line enters the /home/pi/SIM7600X directory and executes the command.
Set the boot initialization script, and run the command:
Add before exit 0 (as shown below):
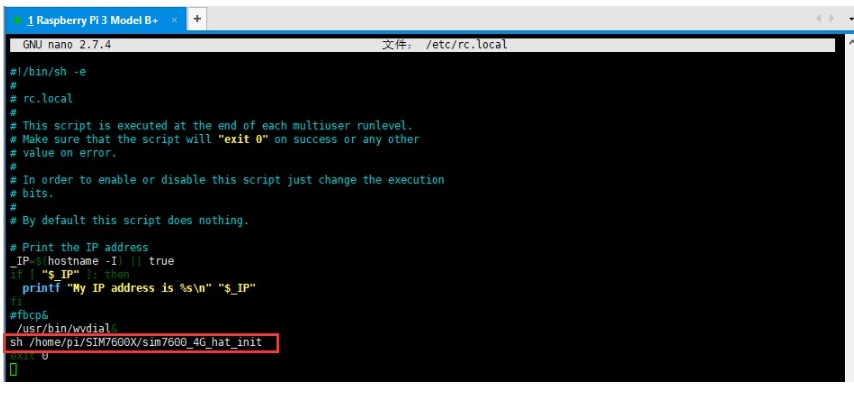
Raspberry Pi serial port configuration
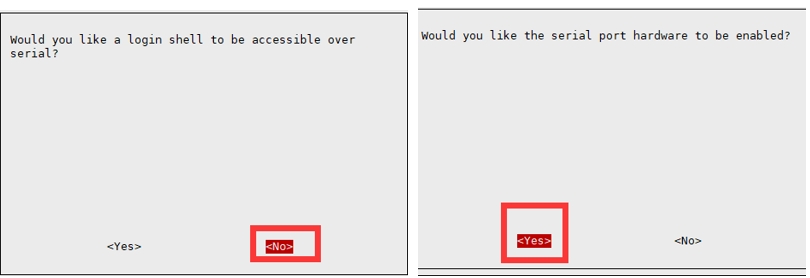
Since the Raspberry Pi serial port is used for terminal debugging by default, if you need to use the serial port, you need to modify the Raspberry Pi settings. Execute the following command to enter the Raspberry Pi configuration:
Select Interfacing Options -> Serial -> no -> yes to disable serial debugging. Open the /boot/config.txt file, and find the following configuration statement to enable the serial port, if not, add it at the end of the file:

Restart to take effect.
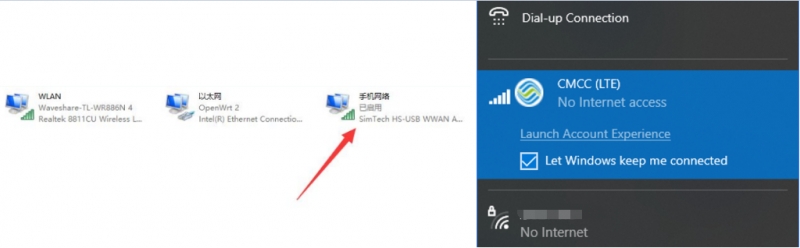
Raspberry Pi minicom serial port debugging
1. Insert the module into the Raspberry Pi. 2. Install minicom, which is a serial debugging tool for the Linux platform:
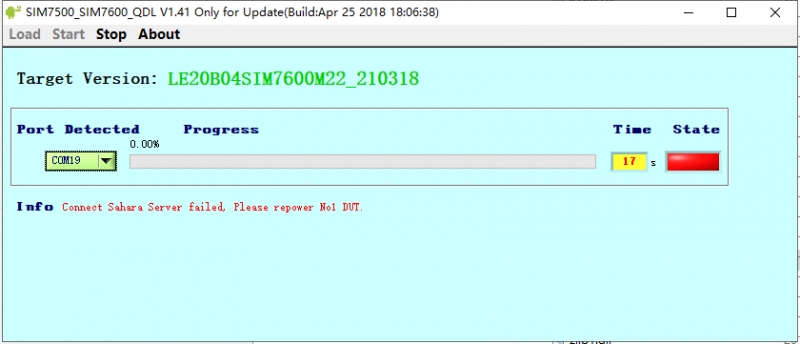
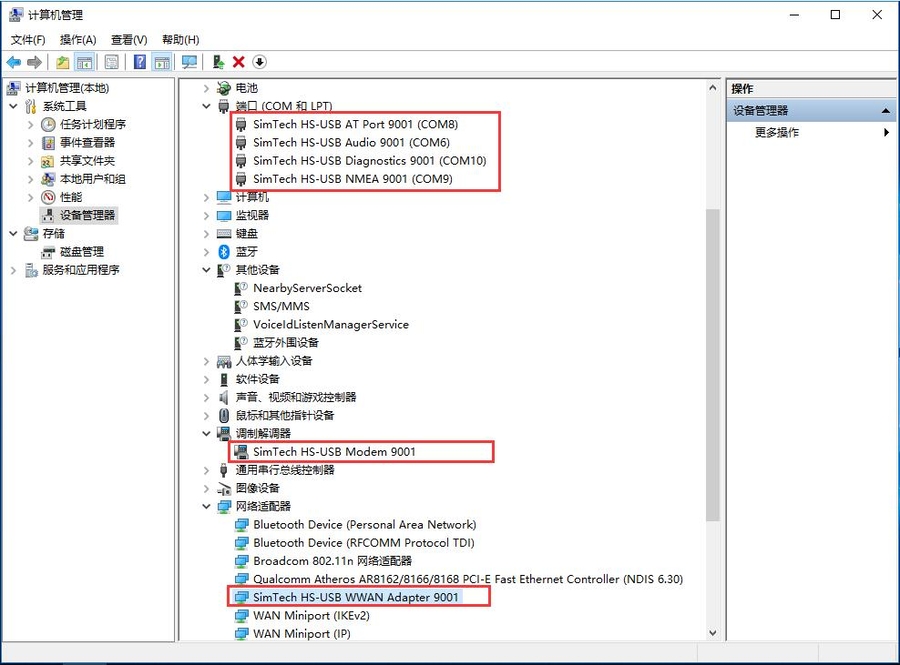
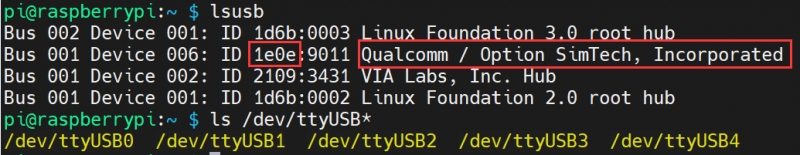
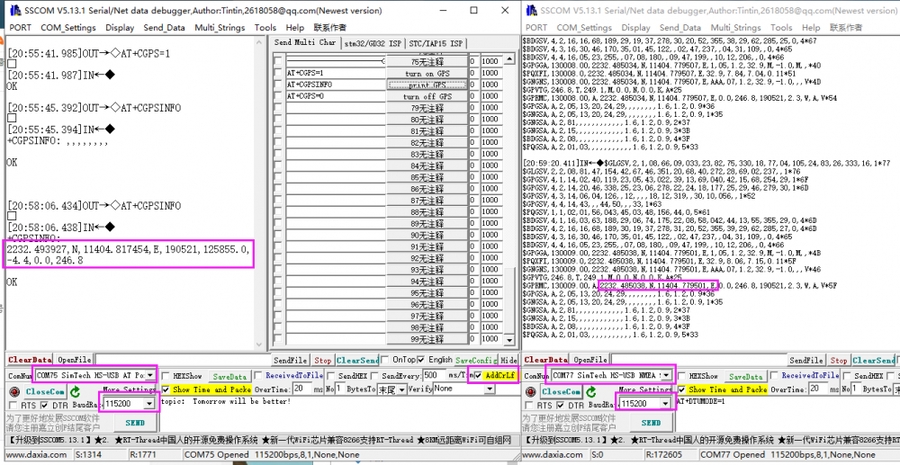
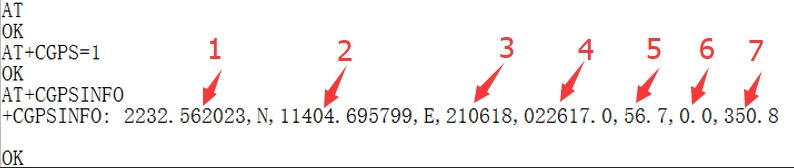
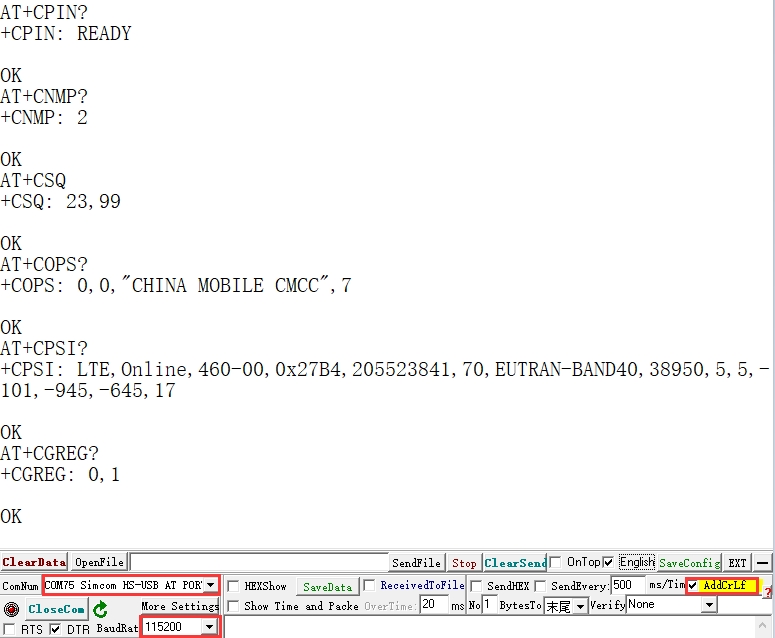
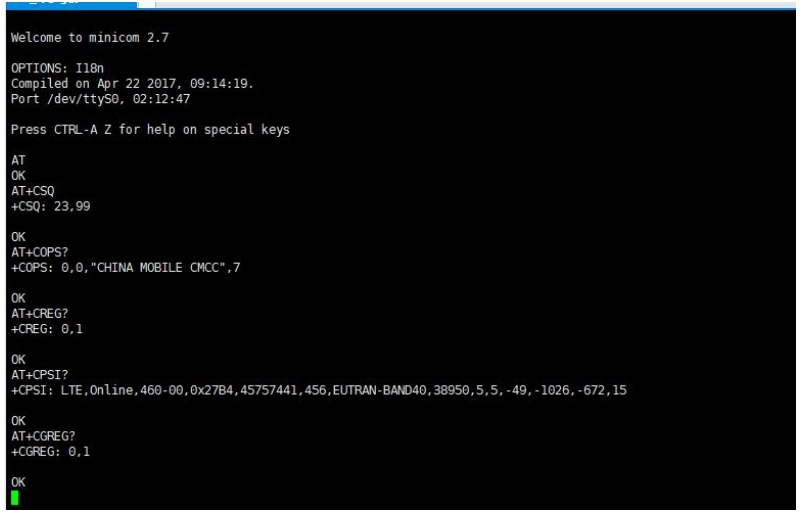
3. Execute minicom -D /dev/ttyS0 (ttyS0 is the serial port of Raspberry Pi 3B/3B+/4B). The default baud rate is 115200. Raspberry Pi 5/2B/zero, the user serial device number is ttyAMA0, and the Raspberry Pi 3B/3B+/4B serial device number is ttyS0. 4. Take the AT synchronization test as an example, and send relevant commands, as shown in the following figure: * minicom can enter setting mode by pressing Ctrl+A, then Z, and select X to exit. 5. Raspberry Pi 5 configures the ttyS0 serial port:
Edit config.txt file:
Add the following and the statement at the end.
You can see ttyS0 after restarting.
Sample Demo
1. Insert the module into the Raspberry Pi. 2. Download the sample demo to the /home/pi/ path:
3. Go to the bcm2835 directory, compile, and install it.
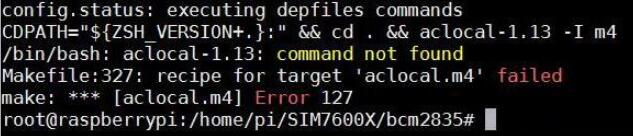
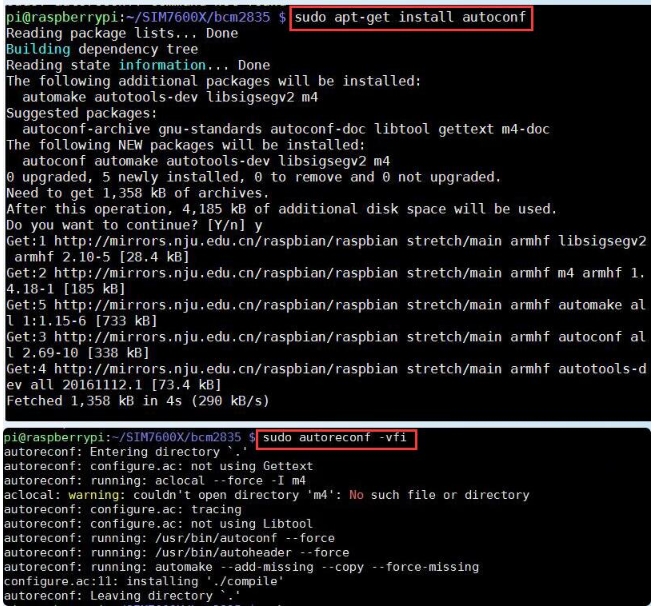
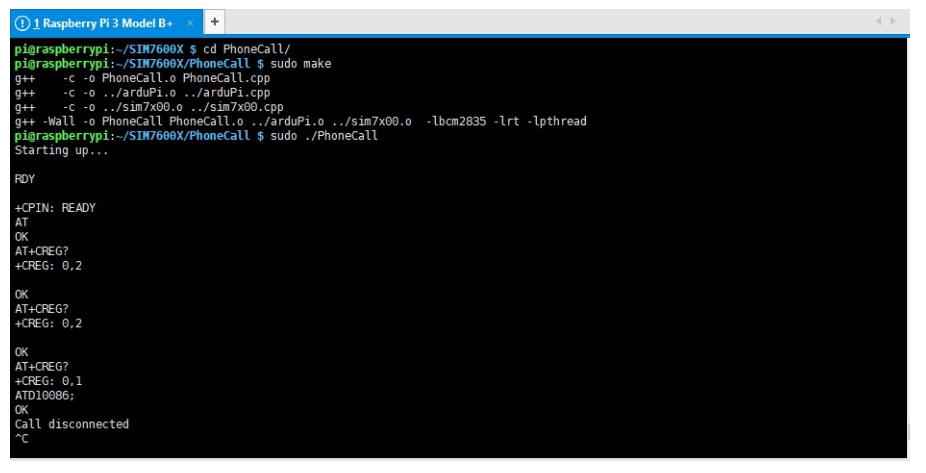
Note: If there is a problem with the compilation, please refer to the instructions in the FAQ. 4. Go to the corresponding instance directory, compile, and run the demo. The relevant instructions are as follows (take the PhoneCall demo as an example):
Use a combination of the above commands:
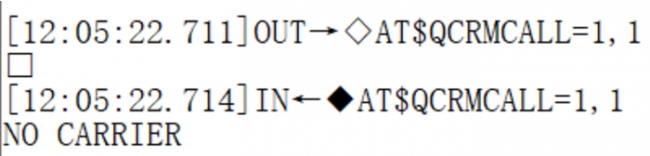
PHONECALL Call Demo
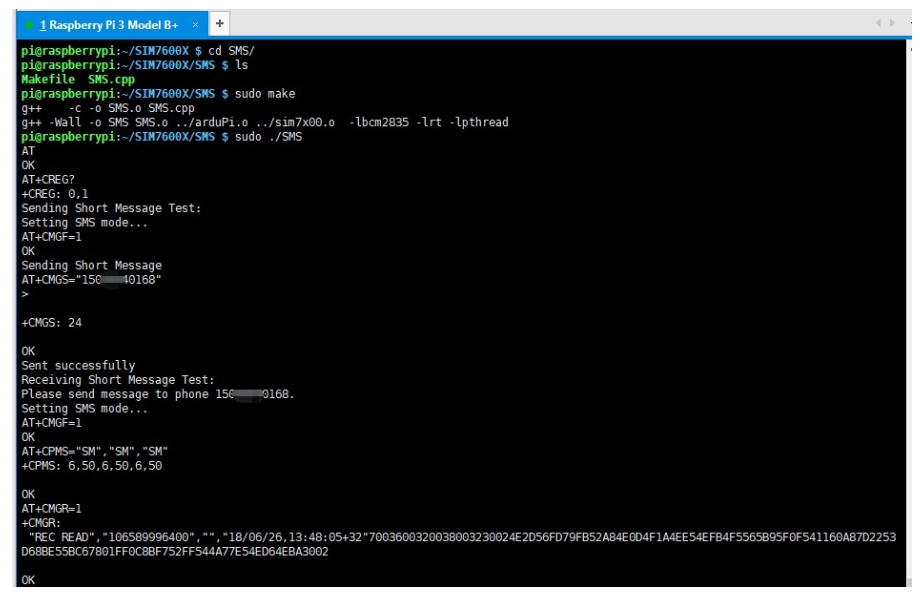
SMS Text Message Sending and Receiving Demo
GPS Positioning Demo
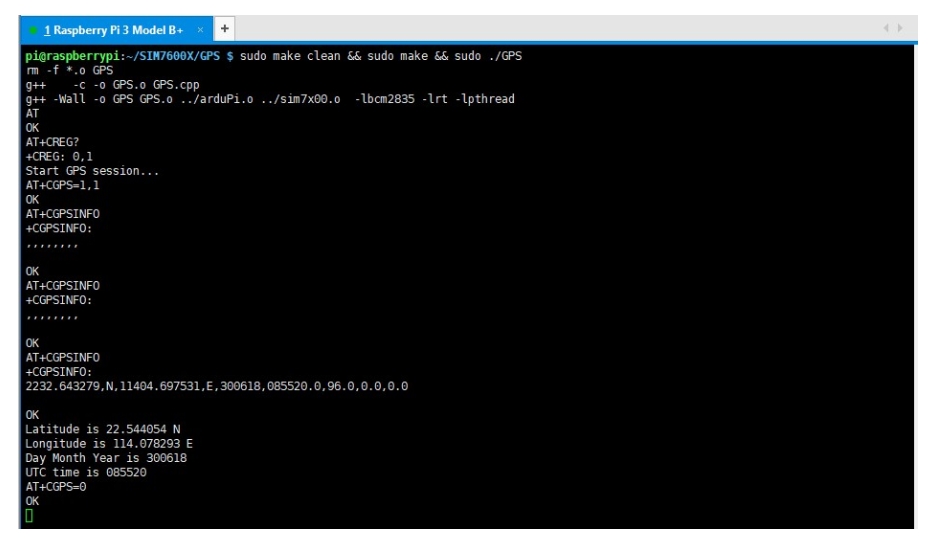
TCP Network Communication Demo
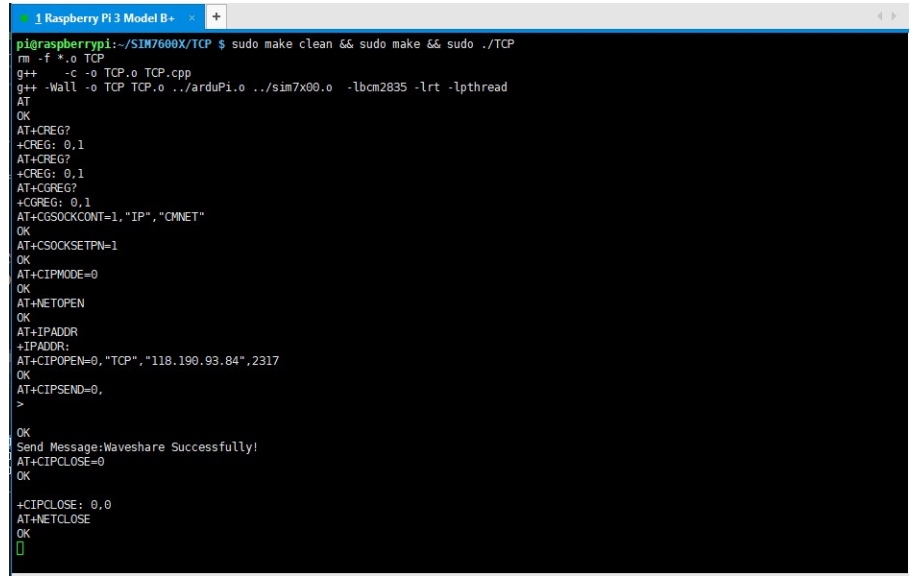
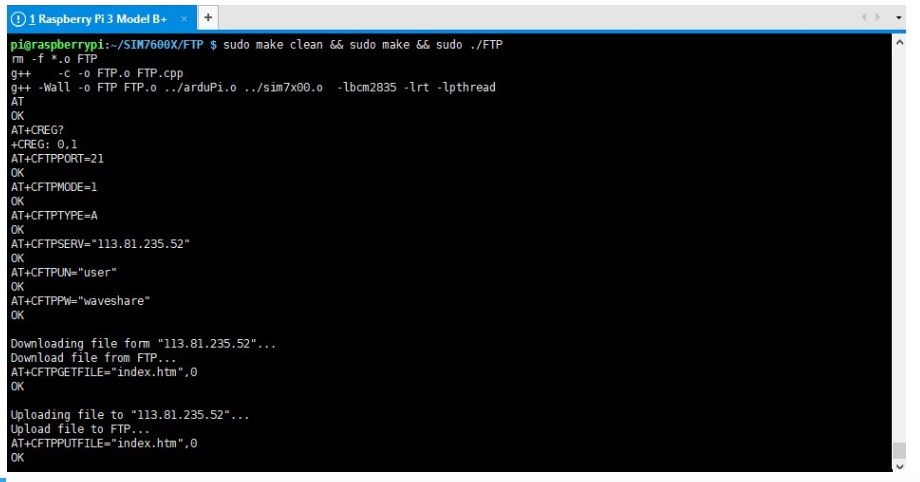
FTP Download and Upload Demos
Arduino Demo
Hardware Connection
Hardware connection to the development board UNO PLUS/Arduino UNO:
5V
5V
GND
GND
TXD
0 (RX)
RXD
1 (TX)
PWR
2
Install Arduino library
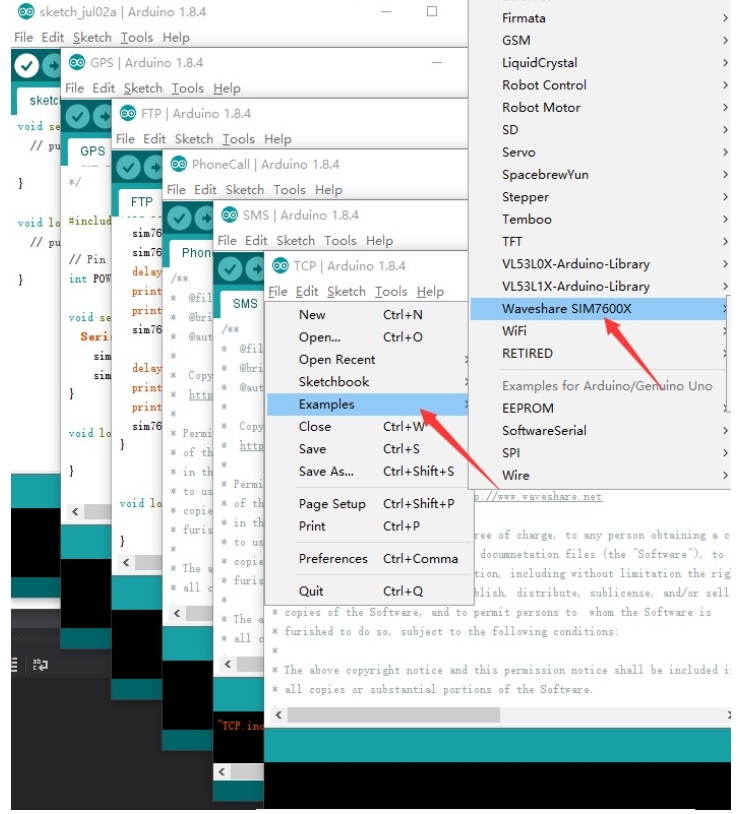
Download the decompression sample demo. Copy the Waveshare_SIM7600X_Arduino_Library folder to the Library directory under the Arduino IDE installation path. Open Arduino IDE --> File --> Examples --> Waveshare SIM7600X, and then choose to run the corresponding example demo:
Sample Demo
PHONECALL Call Demo
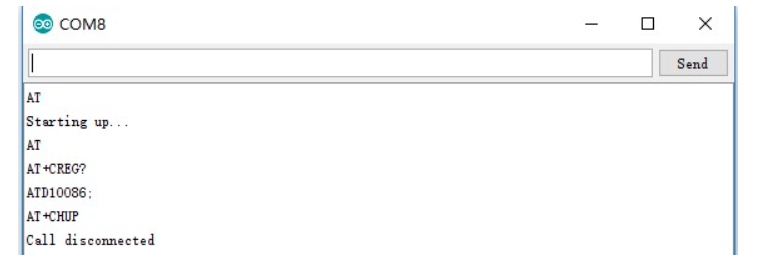
SMS Text Message Sending and Receiving Demo
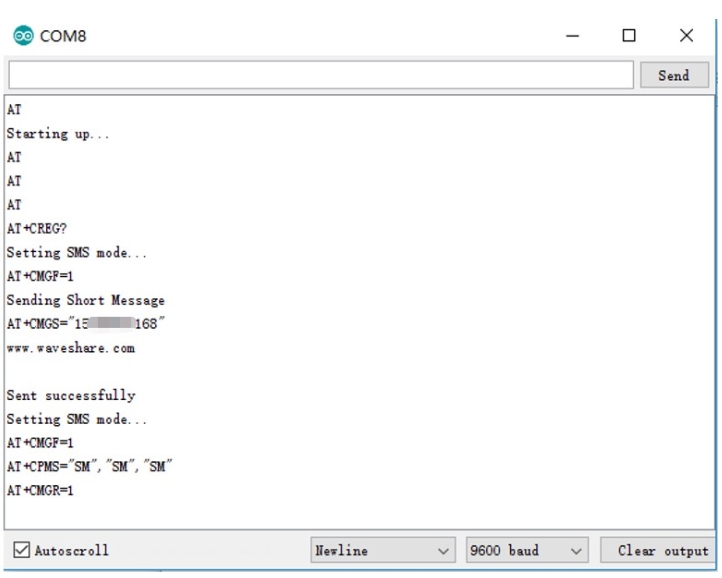
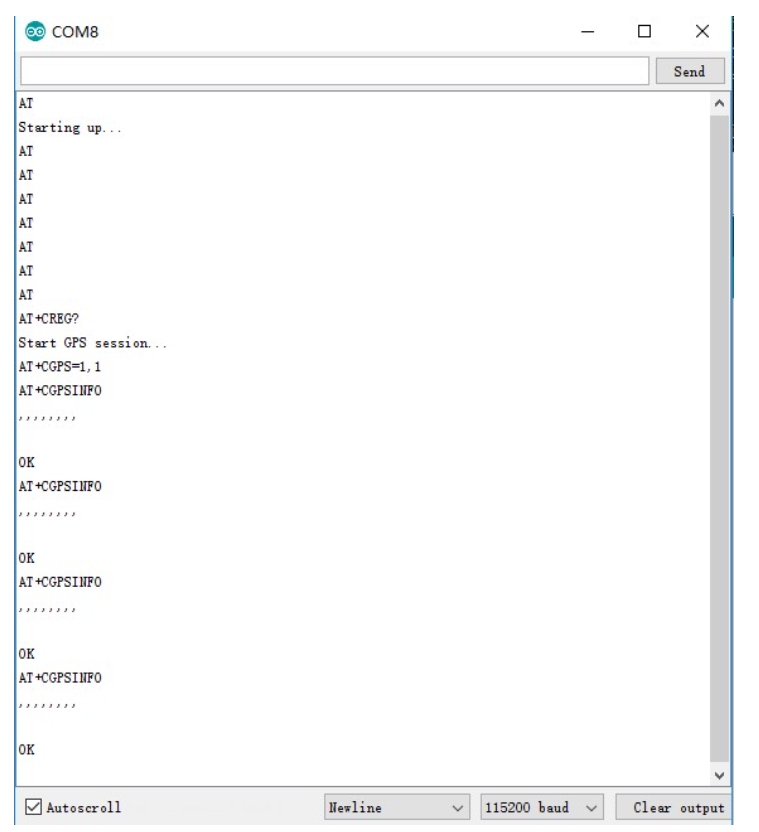
GPS Positioning Demo
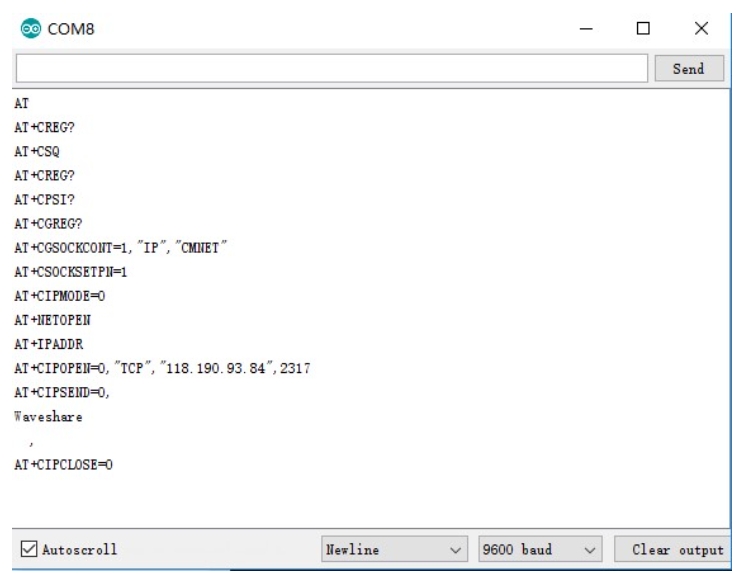
TCP Network Communication Demo
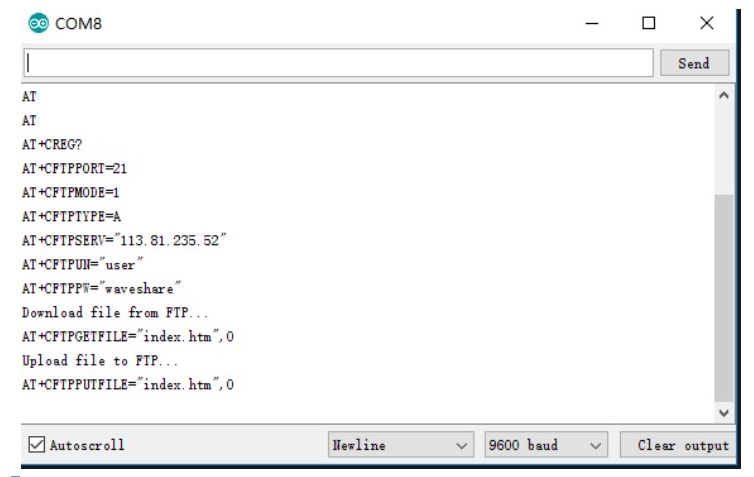
FTP Download and Upload Demo
Jetson Nano Demo
Hardware Connections
Connection diagram

Jetson Nano has an onboard RaspberryPi 40Pin GPIO interface, SIM7600X 4G HAT can be directly connected and used, and Jetson Nano's terminal access the serial port does not affect serial communication with SIM7600X 4G HAT (ie. Pin10 and Pin8).
5V
5V
GND
GND
TXD
10 (Board encoding)
RXD
8 (Board encoding)
PWR
31 (Board code)
Jetson Nano minicom serial port debugging

1. Connect the SIM7600X 4G HAT to the Jetson Nano, press the PWRKER button for three seconds, and then turn it on. 2. Use SERIAL to log in to the Jetson Nano terminal, install minicom, and enter:
3. Run minicom to debug the serial port, and enter in the terminal.
4. Send the AT command to test, press the PWRKEY button for three seconds to start the shutdown, exit the minicom and press Ctrl+A, then X, and finally press ENTER.
Python Demos

After installing the library:
Use the wget tool to download the source code to the specified folder of Jetson Nano, and copy the following command:
Enter the directory where the source code was just created and downloaded, and use the p7zip tool to unzip it to the current directory.
AT

SIM7600X_4G_HAT is connected to Jetson Nano, connected to the antenna, the demo uses the software to power on and off, there is no need to press the button to power on and off, and when you exit, press Ctrl+C to power off the software. Enter the Jetson Nano/AT directory and execute the command:
GPS

SIM7600X_4G_HAT is connected to the Jetson Nano and GNSS antenna. The routine uses software to power on and off. There is no need to press the button to power on and off. When exiting, press Ctrl+C to power off the software. Enter the Jetson Nano/GPS directory and execute the command:
PhoneCall
SIM7600X_4G_HAT is connected to Jetson Nano, the main antenna, and the earphone. The demo uses software to power on and off, no need to press the button to switch on and off. This demo uses the mobile card to automatically dial 10086. Press Ctrl+C when exiting, and the software will start to Shut down. Enter the Jetson Nano/PhoneCall directory and execute the command:

SMS

The SIM7600X_4G_HAT is connected to the Jetson Nano and the main antenna. The demo uses the software to turn it on and off, and there is no need to press the button to turn it on and off. This demo will automatically shut down the software after sending the information www.waveshare.com to the specified number. When users use SMS routines, they must first use tools such as vim to change the number in line 10 of the SMS.py file, replace * with a number, and keep the ' symbol. Enter the Jetson Nano/SMS directory and execute the command:
TCP
The SIM7600X_4G_HAT is connected to the Jetson Nano and the main antenna. The demo uses the software to turn it on and off, and there is no need to press the button to turn it on and off. Enter the Jetson Nano/TCP directory and execute the command:

More sample demos are continuously updated...
FAQ
Last updated
Was this helpful?